Translate this page into:
Marked leukemoid reaction preceded the onset of meningitis: A case report
*Corresponding author: Arjun Kachhwaha, Department of Medical Oncology Haematology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh, Uttarakhand, India. drarjunk95@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Kachhwaha A, Shah B, Satadeve P, Nath UK. Marked leukemoid reaction preceded the onset of meningitis: A case report. J Hematol Allied Sci. 2024;4:117-9. doi: 10.25259/JHAS_55_2024
Abstract
The leukemoid reaction is defined as leukocytosis >50,000/μL, whereas a white blood cell count of more than 11 × 109 leukocytes/L is called leukocytosis. The etiology of leukemoid reactions ranges from benign to hematologic neoplasms and solid malignancies. Identification of the cause is of paramount value in managing leukemoid reactions. Herein, we are reporting a case of a young adult in which marked neutrophilic leukocytosis occurred before the development of meningitis.
Keywords
Leukemoid reaction
Leukocytosis
Hematologic neoplasms
Meningitis
INTRODUCTION
An increase in total leukocyte counts, especially neutrophilic predominance, more than 50,000/μL is a leukemoid reaction.[1] This may precede, coincide, or may develop after the onset of clinical illness. There have been various causes from benign to fatal causes described in literature highlighting the role of close following of and treating the underlying trigger.
CASE REPORT
Here, we are reporting the case of a 48-year-old male, chronic alcoholic, and smoker presented with low backache and abdomen pain for the past 2 months. Physical examination was unremarkable. The baseline hemogram showed anemia with hemoglobin of 7 g/dL, total leukocyte count was 93960/μL, and platelet count was 411000/μL. Red blood cell (RBC) indices were as follows: RBC count: 3.36 × 106/μL, mean corpuscular volume (MCV): 67 fL, mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH): 20.8pg, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC): 31.1 g/dL, and red cell distribution width coefficient of variation (RDW-CV) 17.5%. Peripheral smear showed marked neutrophilic leukocytosis, RBC showed anisopoikilocytosis and predominantly microcytic hypochromic with many target cells and polychromatophils, and platelets were adequate. The corrected reticulocyte count was 1.2%. Breakpoint cluster (Bcr) and abelson (Abl) tyrosine kinase (BCR: ABL1) by polymerase chain reaction of peripheral blood was negative. Liver and renal function tests were within normal limits. Hemoglobin - High-performance liquid chromatography features suggestive of heterozygous beta thalassemia with adult hemoglobin (HbA0): 79.6, HbA2: 6, and HbF: 1.4. Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy showed cellular marrow with trilineage hematopoiesis and cytogenetic was normal karyotype. Patient during evaluation developed acute onset of severe holocranial headache with nausea and vomiting for 7 days and neck rigidity on examination. A lumbar puncture was done. The hemogram showed anemia with hemoglobin of 7.2 g/dL, total leukocyte count was 135590/μL, and platelet count was 386000/μL. Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) was negative, and anti-Hepatitis C virus and anti-human immunodeficiency virus antibodies were nonreactive. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) had a total count of 90 cells/mm3 (100% monomorphic) and was negative for malignant cytology. CSF protein and sugar were 146 and 76 mg/dL, respectively. GeneXpert cartridge-based nucleic acid amplification test (CBNAAT) for Mycobacterium tuberculosis was negative. CSF aerobic and fungal culture was sterile. Magnetic resonance imaging brain showed multiple well-defined variable sized ring enhancing T2/fluid-attenuated inversion recovery hypointense lesions with mild-to-moderate surrounding edema seen in the right frontal and occipital lobes, bilateral temporal-parietal lobes, left caudate, thalamus and right lentiform nuclei, and bilateral cerebella hemispheres, largest of size 20 × 14 mm at right cerebellar hemisphere. On magnetic resonance spectroscopy, lipid-lactate peak was seen and magnetic resonance venography was normal, features were likely of tubercular etiology [Figure 1]. Contrast-enhanced computed tomography thorax and abdomen showed emphysematous changes with bulla formation. Mediational lymphadenopathy and retroperitoneal necrotic lymphadenopathy are likely tubercular etiology. The patient was managed with dexamethasone and antitubercular therapy and had relief in symptoms. The patient was discharged home on oral dexamethasone and antitubercular therapy; unfortunately, the patient died in the next 1 week at home.
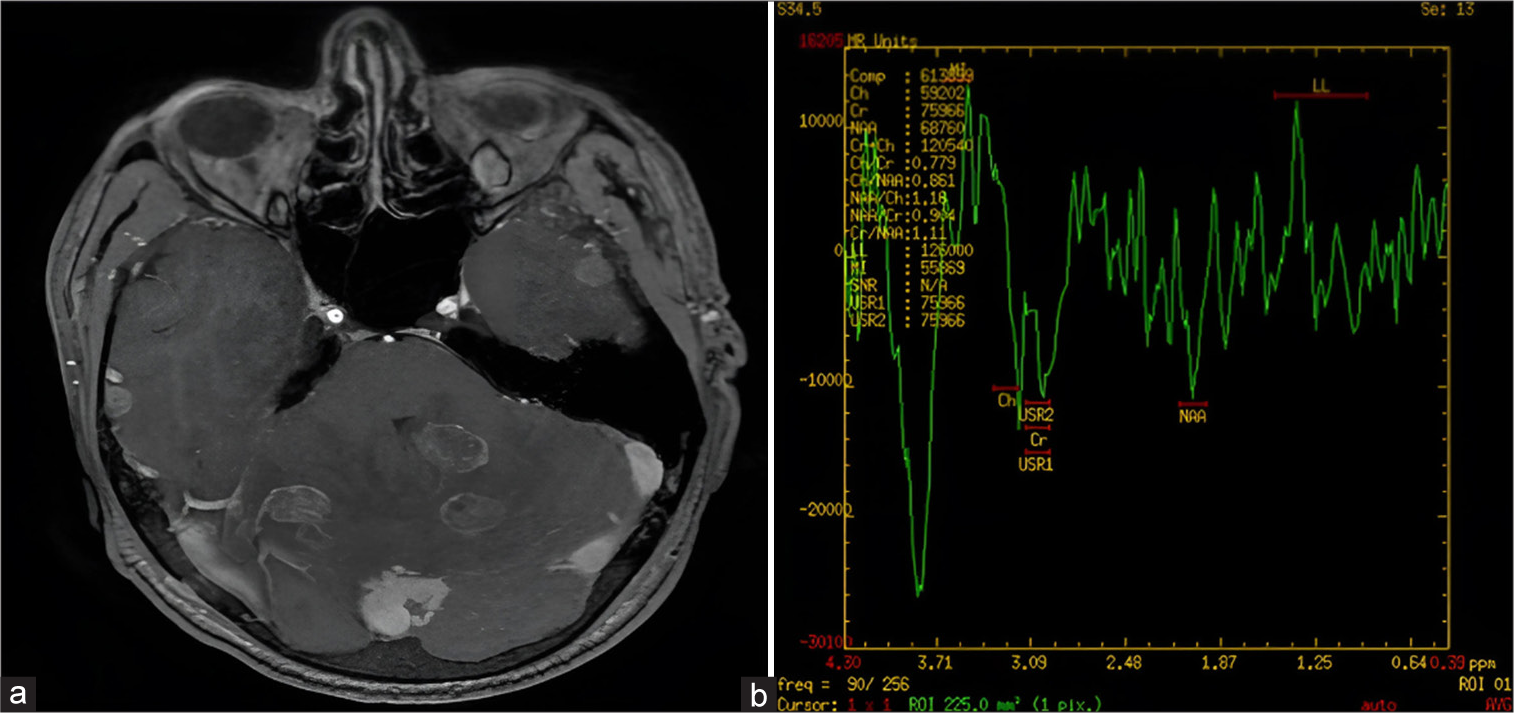
- A 48-year-old male with headache and altered sensorium. (a) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging brain image shows multiple ring-enhancing lesions with mild-to-moderate perilesional edema. (b) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy showing lipid lactate peak.
DISCUSSION
Infections are the most common cause of leukemoid reaction, and tuberculosis is one of them.[2,3] It is imperative to rule out hematological malignancies especially chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and chronic neutrophilic leukemia (CNL) in a case of persistent neutrophilic leucocytosis.[4] Solid organ malignancies have been mentioned to be associated with an extreme degree of leukemoid reaction as a paraneoplastic process in primary malignancies of the esophagus, gallbladder, lung, liver, and pancreas.[1,5]
CONCLUSION
This case highlights the importance of progressive leukocytosis suggesting the development of infection which was later identified as meningitis and became fatal. There is a need to control underlying infection adequately indirectly addressing the rise in total leukocyte counts.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
References
- Paraneoplastic leukemoid reaction in solid tumors. Am J Clin Oncol. 2015;38:326-30.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leukemoid reaction: Spectrum and prognosis of 173 adult patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2013;57:e177-81.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leukemoid reactions to tuberculosis. Arch Intern Med. 1965;116:21-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An update on the etiology and diagnostic evaluation of a leukemoid reaction. Eur J Intern Med. 2006;17:394-8.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Extreme leukocytosis and leukemoid reaction associated with the lung sarcomatoid carcinoma: An unusual case report. Int J Gen Med. 2017;10:7-9.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






